/*
** This file is part of the Interactive Medical Simulation Toolkit (iMSTK)
** iMSTK is distributed under the Apache License, Version 2.0.
** See accompanying NOTICE for details.
*/
#include "FemurObject.h"
#include "imstkCamera.h"
#include "imstkDeviceManager.h"
#include "imstkDeviceManagerFactory.h"
#include "imstkDirectionalLight.h"
#include "imstkKeyboardDeviceClient.h"
#include "imstkKeyboardSceneControl.h"
#include "imstkLevelSetCH.h"
#include "imstkLevelSetModel.h"
#include "imstkMeshIO.h"
#include "imstkMouseDeviceClient.h"
#include "imstkMouseSceneControl.h"
#include "imstkObjectControllerGhost.h"
#include "imstkRbdConstraint.h"
#include "imstkRigidBodyCH.h"
#include "imstkRigidBodyModel2.h"
#include "imstkRigidObject2.h"
#include "imstkRigidObjectController.h"
#include "imstkRigidObjectLevelSetCollision.h"
#include "imstkScene.h"
#include "imstkSceneManager.h"
#include "imstkSimulationManager.h"
#include "imstkSimulationUtils.h"
#include "imstkSurfaceMesh.h"
#include "imstkVisualModel.h"
#include "imstkVolumeRenderMaterial.h"
#include "imstkVTKViewer.h"
#ifndef iMSTK_USE_HAPTICS
#include "imstkDummyClient.h"
#include "imstkMouseDeviceClient.h"
#endif
using namespace imstk;
std::shared_ptr<RigidObject2>
makeRigidObj(const std::string& name)
{
auto rbdModel = std::make_shared<RigidBodyModel2>();
rbdModel->getConfig()->m_maxNumIterations = 8;
rbdModel->getConfig()->m_velocityDamping = 1.0;
rbdModel->getConfig()->m_angularVelocityDamping = 1.0;
rbdModel->getConfig()->m_maxNumConstraints = 40;
rbdModel->getConfig()->m_gravity = Vec3d::Zero();
// Create the first rbd, plane floor
auto rigidObj = std::make_shared<RigidObject2>(name);
auto toolMesh = MeshIO::read<SurfaceMesh>(iMSTK_DATA_ROOT "/Surgical Instruments/Scalpel/Scalpel_Hull_Subdivided_Shifted.stl");
toolMesh->rotate(Vec3d(0.0, 1.0, 0.0), 3.14, Geometry::TransformType::ApplyToData);
toolMesh->rotate(Vec3d(1.0, 0.0, 0.0), -1.57, Geometry::TransformType::ApplyToData);
toolMesh->scale(Vec3d(0.07, 0.07, 0.07), Geometry::TransformType::ApplyToData);
auto material = std::make_shared<RenderMaterial>();
material->setDisplayMode(RenderMaterial::DisplayMode::Surface);
material->setShadingModel(RenderMaterial::ShadingModel::PBR);
material->setMetalness(0.9);
material->setRoughness(0.4);
material->setDiffuseColor(Color(0.7, 0.7, 0.7));
// Create the object
rigidObj->setVisualGeometry(toolMesh);
rigidObj->setPhysicsGeometry(toolMesh);
rigidObj->setCollidingGeometry(toolMesh);
rigidObj->setDynamicalModel(rbdModel);
rigidObj->getVisualModel(0)->setRenderMaterial(material);
rigidObj->getRigidBody()->m_mass = 10.0;
rigidObj->getRigidBody()->m_intertiaTensor = Mat3d::Identity() * 10000.0;
rigidObj->getRigidBody()->m_initPos = Vec3d(0.0, 1.0, 2.0);
// Add a component for controlling via another device
auto controller = rigidObj->addComponent<RigidObjectController>();
controller->setControlledObject(rigidObj);
controller->setLinearKs(50000.0);
controller->setAngularKs(300000000.0);
controller->setUseCritDamping(true);
controller->setForceScaling(0.005);
controller->setTranslationOffset(Vec3d(0.4, 0.7, 1.6));
controller->setSmoothingKernelSize(30);
// Add extra component to tool for the ghost
auto controllerGhost = rigidObj->addComponent<ObjectControllerGhost>();
controllerGhost->setUseForceFade(true);
controllerGhost->setController(controller);
return rigidObj;
}
///
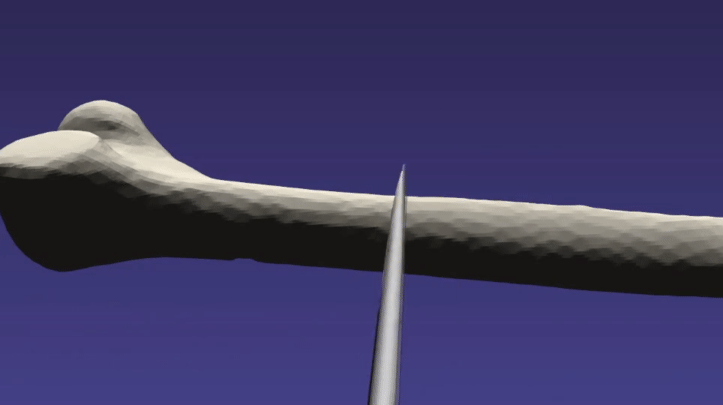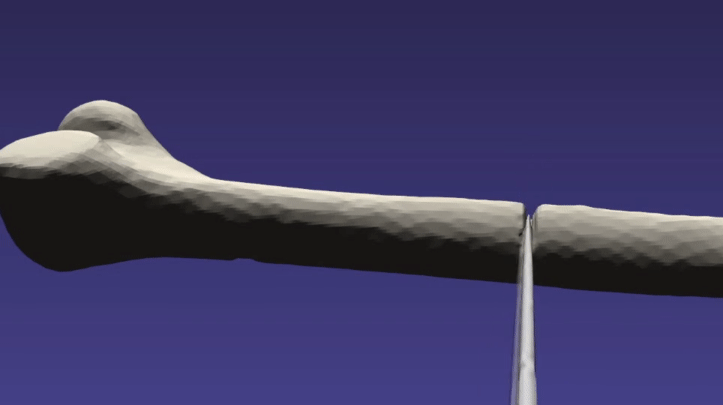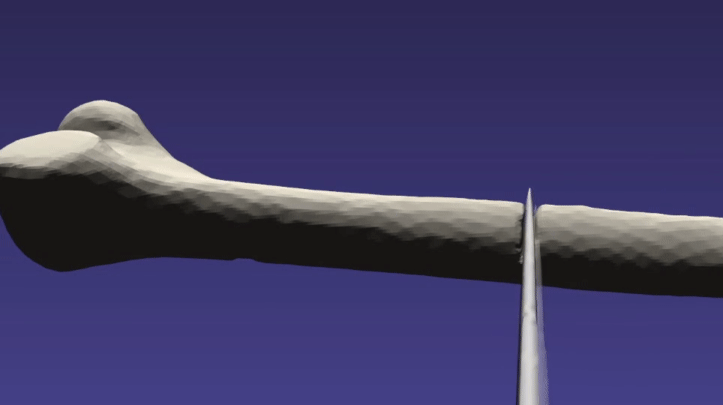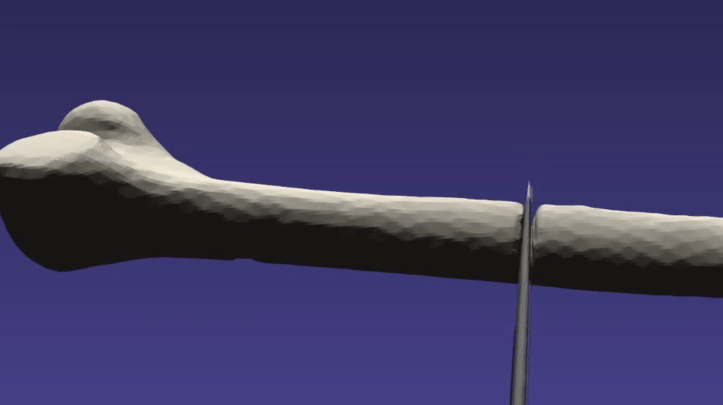
/// \brief This example demonstrates cutting a femur bone with a tool
/// Some of the example parameters may need to be tweaked for differing
/// systems
///
int
main()
{
// Setup logger (write to file and stdout)
Logger::startLogger();
auto scene = std::make_shared<Scene>("FemurCut");
// Setup the Femur
auto femurObj = std::make_shared<FemurObject>();
scene->addSceneObject(femurObj);
// Setup the tool that cuts the femur
std::shared_ptr<RigidObject2> rbdObj = makeRigidObj("ToolObject");
scene->addSceneObject(rbdObj);
// Setup cutting interaction between level set femur and rigid object tool
auto cutting = std::make_shared<RigidObjectLevelSetCollision>(rbdObj, femurObj);
{
auto colHandlerA = std::dynamic_pointer_cast<RigidBodyCH>(cutting->getCollisionHandlingA());
colHandlerA->setUseFriction(false);
colHandlerA->setBaumgarteStabilization(0.05); // inelastic collision
auto colHandlerB = std::dynamic_pointer_cast<LevelSetCH>(cutting->getCollisionHandlingB());
colHandlerB->setLevelSetVelocityScaling(0.01);
colHandlerB->setKernel(3, 1.0);
//colHandlerB->setLevelSetVelocityScaling(0.0); // Can't push the levelset
colHandlerB->setUseProportionalVelocity(true);
}
scene->addInteraction(cutting);
// Light
auto light = std::make_shared<DirectionalLight>();
light->setDirection(Vec3d(0.0, -8.0, -5.0));
light->setIntensity(1.0);
scene->addLight("light", light);
// Adjust camera
scene->getActiveCamera()->setFocalPoint(0.25, 0.83, 1.58);
scene->getActiveCamera()->setPosition(0.243, 1.06, 1.95);
scene->getActiveCamera()->setViewUp(0.05, 0.86, -0.51);
{
auto viewer = std::make_shared<VTKViewer>();
viewer->setVtkLoggerMode(VTKViewer::VTKLoggerMode::MUTE);
viewer->setActiveScene(scene);
// Add a module to run the scene
auto sceneManager = std::make_shared<SceneManager>();
sceneManager->setActiveScene(scene);
auto driver = std::make_shared<SimulationManager>();
driver->addModule(viewer);
driver->addModule(sceneManager);
driver->setDesiredDt(0.001); // Exactly 1000ups
#ifdef iMSTK_USE_HAPTICS
// Setup default haptics manager
std::shared_ptr<DeviceManager> hapticManager = DeviceManagerFactory::makeDeviceManager();
driver->addModule(hapticManager);
std::shared_ptr<DeviceClient> deviceClient = hapticManager->makeDeviceClient();
#else
auto deviceClient = std::make_shared<DummyClient>();
connect<Event>(sceneManager, &SceneManager::postUpdate, [&](Event*)
{
const Vec2d mousePos = viewer->getMouseDevice()->getPos();
const Vec3d worldPos = Vec3d(mousePos[0] * 0.5 - 0.5, mousePos[1] * 0.2 + 0.1, -0.025);
deviceClient->setPosition(worldPos);
});
#endif
auto controller = rbdObj->getComponent<RigidObjectController>();
controller->setDevice(deviceClient);
std::shared_ptr<ObjectControllerGhost> ghostObj = rbdObj->addComponent<ObjectControllerGhost>();
ghostObj->setController(controller);
connect<Event>(sceneManager, &SceneManager::preUpdate,
[&](Event*)
{
rbdObj->getRigidBodyModel2()->getConfig()->m_dt = sceneManager->getDt();
femurObj->getLevelSetModel()->getConfig()->m_dt = sceneManager->getDt();
});
// Add default mouse and keyboard controls to the viewer
std::shared_ptr<Entity> mouseAndKeyControls =
SimulationUtils::createDefaultSceneControl(driver);
scene->addSceneObject(mouseAndKeyControls);
driver->start();
}
return 0;
}